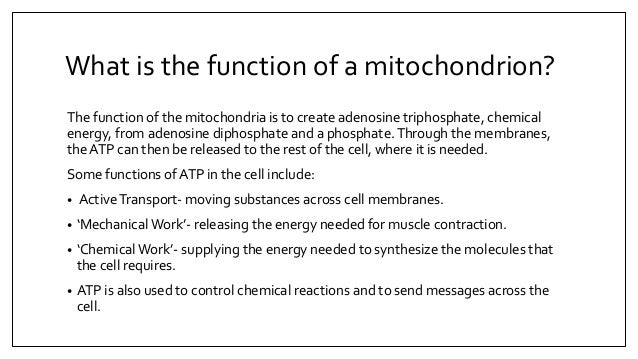
Explain the structure and function of the mitochondria pdf Werris Creek
Explain the structure and function? Yahoo Answers Mitochondria are eukaryotic organelles involved in many metabolic pathways, but their principal function is the generation of most of the cellular ATP through the oxidative phosphorylation system (OXPHOS) (Attardi & Schatz, 1988). From the point of view of their biogenesis, mitochondria are unique organelles since they require the contribution of two physically separated genomes. The …
Biology Essential Standard 1.1 Understand the relationship
ATP Synthase Definition Structure & Function Study.com. Functions of mitochondria: Mitochondria has an important function is to harvest energy. The simpler compounds obtained from nutrition are carried to the mitochondria where they are further processed and converted to charged molecules., Mitochondrial structure and function are central to cell physiology and are mutually interdependent. Mitochondria represent a primary target of the alcohol-induced tissue injury, particularly in.
Centrosome: Microtubules sprout from this structure, which is located next to the nucleus and is composed of two centrioles — arrays of microtubules — that function in separating genetic material during cell division. Each mitochondrion is a double membrane bound structure with the outer membrane and the inner membrane dividing its lumen distinctly into two aqueous compartments, i.e., the outer compartment and the inner compartment.
explain the term karyotype and mention the karyotype analysis and its significance. BIOLOGY MODULE - 1 Cell – Structure and Function Diversity and Evolution of Life 78 Notes 4.1 THE CELL AND CELL THEORY 4.1.1 Landmarks in cell study Soon after Anton van Leewenhock invented the microscope, Robert Hooke in 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be … A mitochondrion produces energy for a cell. Mitochondria (the plural of mitochondrion) are small organelles found in most nucleated cells, including those of plants, animals and fungi.
The Role of Mitochondria in Cancer and Other Chronic Diseases Mitochondria Structure and Roles The number of mitochondria per cell is energy/function dependent; i.e., those cells that require and expend the most energy contain the highest number of mitochondria. Most cells have between a few hundred to over 20,000 mitochondria; they are concen-trated most heavily in cells of the heart Mitochondria structure is quite compact, and all of its functions happen within this structure. Structure of mitochondria They are sac-like double membranes structures …
21/01/2009В В· Mitochondria : It is a semi autonomous cell organelle, main function is ATP production i.e energy coin. so considered as POWER HOUSE of the cell. Plastids : It is also a semi autonomous cell organelle found in plant cells, main function is photosynthesis. Mitochondria vs Chloroplast The major difference between mitochondria and chloroplast is that the latter contains thylakoid membranes and pigment molecules, whereas the mitochondria membranes contain respiratory enzymes not found in chloroplast membranes.
Structure of Mitochondria The cytoplasm of nearly all eukaryotic cells contain mitochondria, although there is at least one exception, the protist Chaos (Pelomyxa) carolinensis . They are especially abundant in cells and parts of cells that are associated with active processes. Mitochondria are present in the living eucaryotic cells as membrane bound organelles essential for cellular respiВration. Although quite variable in shape, mitochondria are generally sauВsage-shaped, spherical, oval, pearВshaped, cylindrical or filamentous mitochondrion are not uncommon.
Cell Structure Worksheet Objectives: After working through this worksheet, you should: a) Understand the basic structure of a typical eukaryotic cell. b) Know the structure and function of the plasma membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, vesicles, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria and chloroplasts. c) Be able to label a diagram of a typical Organelle Structure and Function. Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are called Organelles. The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by an electron microscope) is called the cell’s ultrastructure. Organelles perform different functions within a cell, and this is
Overall, the researchers found no difference in the density, size or shape of mitochondria in patients, nor in several other aspects of their structure and function, although the cristae (protrusions of the membranes inside the mitochondria) were more condensed than usual. However, despite this vast range in size, shape, and function, all these little factories have the same basic machinery. There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do.
Centrosome: Microtubules sprout from this structure, which is located next to the nucleus and is composed of two centrioles — arrays of microtubules — that function in separating genetic material during cell division. 19/10/2008 · Best Answer: The outer membrane covers the organelle and contains it. The inner membrane folds over many times (cristae). That folding increases the surface area inside the organelle. Many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The increased surface area allows the small
The most rational approach is to understand the mechanisms underlying mitochondrial damage for specific medications and attempt to counteract their deleterious effects with nutritional therapies. This article reviews our basic understanding of how mitochondria function and how medications dam- Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. They are small structures within a cell that are made up of two membranes and a matrix. The membrane is where the chemical reactions occur and the matrix is where the fluid is held. Mitochondria are a part of eukaryotic cells. The
Mitochondria cannot function in an anaerobic environment. Training in zone 2 is the best way to develop more mitochondria. Know your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold and use your heart monitor to keep that oxygen flowing freely to your cells. 13. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion and explain the importance of compartmentalization in mitochondrial function.-Mitochondria are the sites of cellular respiration, chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis, they are not part of the endomembrane system.
A mitochondrion produces energy for a cell. Mitochondria (the plural of mitochondrion) are small organelles found in most nucleated cells, including those of plants, animals and fungi. Ultra structure of Mitochondria: Mitochondria is a double membrane bound organelle of the cell which has two compartments (outer and inner). The outer membrane is separated by a space of 6-8 nm from the inner membrane.
Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition. The mitochondrion is a double membrane organelle found in eukaryotic cells, responsible for ATP production. Its size range Its size range between 1µm – a few µm, may be individual or branched, have a tubular network and may change shape., Organelle Structure and Function. Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are called Organelles. The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by an electron microscope) is called the cell’s ultrastructure. Organelles perform different functions within a cell, and this is.
Relationship Between Cell Structure & Function Sciencing

Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition. In the same way that the main building controls a gigantic factory, the nucleus is the control center of the cell. This organelle holds the cell's DNA and the directions for …, Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition Papers Presented at the First Colloquium of the Johnson Research Foundation of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, April 13, 1963.
Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition. The Role of Mitochondria in Cancer and Other Chronic Diseases Mitochondria Structure and Roles The number of mitochondria per cell is energy/function dependent; i.e., those cells that require and expend the most energy contain the highest number of mitochondria. Most cells have between a few hundred to over 20,000 mitochondria; they are concen-trated most heavily in cells of the heart, Suggest which pellet, A, B or C contained the mitochondria. (d) People with mitochondrial disease have mitochondria that do not function properly. Some people with mitochondrial disease can ….
Explain how the structure of the mitochondrion is adapted

What are the Structure and function of mitochondria?. Each mitochondrion is a double membrane bound structure with the outer membrane and the inner membrane dividing its lumen distinctly into two aqueous compartments, i.e., the outer compartment and the inner compartment. Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition Papers Presented at the First Colloquium of the Johnson Research Foundation of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, April 13, 1963.
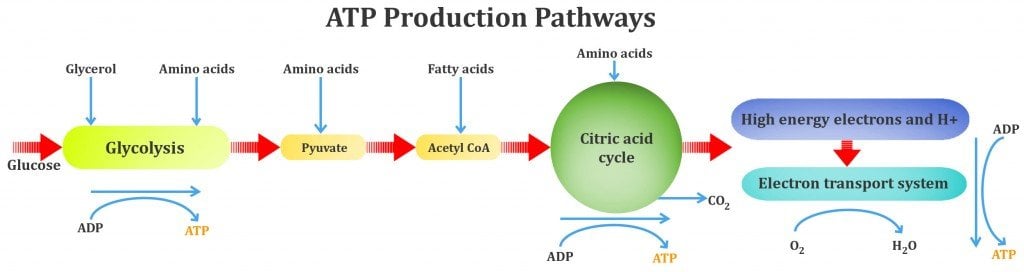
The mitochondrion is a double membrane organelle found in eukaryotic cells, responsible for ATP production. Its size range Its size range between 1µm – a few µm, may be individual or branched, have a tubular network and may change shape. To explain the function of spores in terms of chemical and heat resistance To describe characteristics of different types of membrane transport To describe the exact cellular location and serological classification as O antigen of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) To explain how the structure of LPS confers antigenic specificity and toxicity To describe the exact cellular location of Lipid A To explain
The Role of Mitochondria in Cancer and Other Chronic Diseases Mitochondria Structure and Roles The number of mitochondria per cell is energy/function dependent; i.e., those cells that require and expend the most energy contain the highest number of mitochondria. Most cells have between a few hundred to over 20,000 mitochondria; they are concen-trated most heavily in cells of the heart 16/03/2016В В· Mitochondria structure and function-This lecture explains about the structure and function of mitochondria. This lecture will explain the structure and functions of mitochondria.
Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition Papers Presented at the First Colloquium of the Johnson Research Foundation of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, April 13, 1963 Mitochondria is a special cell that in inside another cell. The function of the mitochondria is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
MITOCHONDRIAL DNA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION mitochondria. ATA codes for methionine in mitochondria but isoleucine in the cytosol. Finally, AGA or AGG in mitochondria code for a stop codon instead of However, despite this vast range in size, shape, and function, all these little factories have the same basic machinery. There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do.
Cell Structure and Function Standard B-2.1: Recall the three major tenets of cell theory Standard B-2.2 : Summarize the structures and functions of organelles found in a The transverse tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum systems. Adapted, by permission, from G.R. Hunter and R.T. Harris, 2008, Structure and function of the muscular
Mitochondria cannot function in an anaerobic environment. Training in zone 2 is the best way to develop more mitochondria. Know your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold and use your heart monitor to keep that oxygen flowing freely to your cells. Overall, the researchers found no difference in the density, size or shape of mitochondria in patients, nor in several other aspects of their structure and function, although the cristae (protrusions of the membranes inside the mitochondria) were more condensed than usual.
Mitochondrial structure and function are central to cell physiology and are mutually interdependent. Mitochondria represent a primary target of the alcohol-induced tissue injury, particularly in Mitochondria are eukaryotic organelles involved in many metabolic pathways, but their principal function is the generation of most of the cellular ATP through the oxidative phosphorylation system (OXPHOS) (Attardi & Schatz, 1988). From the point of view of their biogenesis, mitochondria are unique organelles since they require the contribution of two physically separated genomes. The …
Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition Papers Presented at the First Colloquium of the Johnson Research Foundation of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, April 13, 1963 The transverse tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum systems. Adapted, by permission, from G.R. Hunter and R.T. Harris, 2008, Structure and function of the muscular
The Role of Mitochondria in Cancer and Other Chronic Diseases Mitochondria Structure and Roles The number of mitochondria per cell is energy/function dependent; i.e., those cells that require and expend the most energy contain the highest number of mitochondria. Most cells have between a few hundred to over 20,000 mitochondria; they are concen-trated most heavily in cells of the heart Centrosome: Microtubules sprout from this structure, which is located next to the nucleus and is composed of two centrioles — arrays of microtubules — that function in separating genetic material during cell division.
The wall of a microtubule is composed of 13 parallel protofilaments that enclose a central lumen about 150 A 0 wide. Each protofilaments is made up of a row of globular subunits formed mainly of protein tubulin, each contains one alpha-tubulin molecule and one beta-tubulin molecule. Cell Structure Worksheet Objectives: After working through this worksheet, you should: a) Understand the basic structure of a typical eukaryotic cell. b) Know the structure and function of the plasma membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, vesicles, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria and chloroplasts. c) Be able to label a diagram of a typical

Within each circle, explain the life function labeled in that circle. Draw a picture depicting the life Draw a picture depicting the life function next to each circle. Within each circle, explain the life function labeled in that circle. Draw a picture depicting the life Draw a picture depicting the life function next to each circle.
Is mitochondrial function abnormal? ME Research UK

Explain the structure and function? Yahoo Answers. Structure of Mitochondria The cytoplasm of nearly all eukaryotic cells contain mitochondria, although there is at least one exception, the protist Chaos (Pelomyxa) carolinensis . They are especially abundant in cells and parts of cells that are associated with active processes., What is the Structure and Function of the Golgi Apparatus Golgi apparatus : Golgi bodies are absent in prokaryotic cells. Golgi complex is found in all eukaryotic cells except RBCs. Historical Account : Camillo Golgi (1898), a zoologist, observed Golgi bodies in the form of a network in nerve cells of barn owl. Ultrastructure : […].
Mitochondria Structure and Function YouTube
Mitochondria Structure and Function YouTube. 16/03/2016В В· Mitochondria structure and function-This lecture explains about the structure and function of mitochondria. This lecture will explain the structure and functions of mitochondria., Each mitochondrion is a double membrane bound structure with the outer membrane and the inner membrane dividing its lumen distinctly into two aqueous compartments, i.e., the outer compartment and the inner compartment..
While mitochondria have many functions, remember that their main function is the production of energy currency called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and that the process by which mitochondria Within each circle, explain the life function labeled in that circle. Draw a picture depicting the life Draw a picture depicting the life function next to each circle.
Mitochondria are eukaryotic organelles involved in many metabolic pathways, but their principal function is the generation of most of the cellular ATP through the oxidative phosphorylation system (OXPHOS) (Attardi & Schatz, 1988). From the point of view of their biogenesis, mitochondria are unique organelles since they require the contribution of two physically separated genomes. The … Ultra structure of Mitochondria: Mitochondria is a double membrane bound organelle of the cell which has two compartments (outer and inner). The outer membrane is separated by a space of 6-8 nm from the inner membrane.
However, despite this vast range in size, shape, and function, all these little factories have the same basic machinery. There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do. 19/10/2008В В· Best Answer: The outer membrane covers the organelle and contains it. The inner membrane folds over many times (cristae). That folding increases the surface area inside the organelle. Many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The increased surface area allows the small
Centrosome: Microtubules sprout from this structure, which is located next to the nucleus and is composed of two centrioles — arrays of microtubules — that function in separating genetic material during cell division. The Structure and Functions of Mitochondria CI CII CIII CIV NADH NAD++H+ CV FADH2 FAD++2H+ O2 H2O Prohibitin COX IV UCP ROS ROS ROS ROS SOD ROS TXNRD2 ANT ADP P VDAC HK ADP P Pi Fatty Acid Biosynthesis: UCP1 UCP2 SDHA UCP3 SDHB SDHC SDHD Cyt-C Cyt-C Reductase ATP Synthase acetyl CoA yme A TCA Cycle ADP NAD + D H2 CO2 P NADH …
Chloroplasts work in conjunction with mitochondria, which is the other organelle required for photosynthesis. While chloroplasts create energy, mitochondria aid in plant respiration. Chloroplasts and mitochondria are both unique from other cell structures because they contain their own DNA and can function independently of their parent cell. Here are the Structure and function of mitochondria. The number of Mc varies with the cell type and functional stages. In eukaryotes, approximately 2000 Mc copies one-fifth of its total cell volume.
The mitochondrion is a double membrane organelle found in eukaryotic cells, responsible for ATP production. Its size range Its size range between 1µm – a few µm, may be individual or branched, have a tubular network and may change shape. Mitochondria are organelles located in the cells of each complex organism. These organelles are shaped in a rod-like structure located in both plant and animal cells, and they create around 90% of the chemical energy which cells need in order to survive.
Functions of mitochondria: Mitochondria has an important function is to harvest energy. The simpler compounds obtained from nutrition are carried to the mitochondria where they are further processed and converted to charged molecules. The ribosomes in the matrix are similar in structure to ribosomes found in bacteria. This and the nature of mitochondrial DNA suggests that mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that took up
Cell Structure Worksheet Objectives: After working through this worksheet, you should: a) Understand the basic structure of a typical eukaryotic cell. b) Know the structure and function of the plasma membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, vesicles, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria and chloroplasts. c) Be able to label a diagram of a typical Explain how the structure of each organelle determines it function. (Example: folded inner membrane in (Example: folded inner membrane in mitochondria increases surface area for energy production during aerobic cellular respiration).
The mitochondrion is a double membrane organelle found in eukaryotic cells, responsible for ATP production. Its size range Its size range between 1µm – a few µm, may be individual or branched, have a tubular network and may change shape. vi State one function of each of the following organelles and explain how these functions are related to each other. 1 mark per explanation) Explain how structure is related to function for each of the following organelles: a) mitochondrion (3 marks) b) chloroplast (3 marks) c) rough endoplasmic reticulum (3 marks) State one way in which the following organelles work together: a) lysosomes and
Centrosome: Microtubules sprout from this structure, which is located next to the nucleus and is composed of two centrioles — arrays of microtubules — that function in separating genetic material during cell division. The ribosomes in the matrix are similar in structure to ribosomes found in bacteria. This and the nature of mitochondrial DNA suggests that mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that took up
ATP Synthase Definition Structure & Function Study.com

Relationship Between Cell Structure & Function Sciencing. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. They are small structures within a cell that are made up of two membranes and a matrix. The membrane is where the chemical reactions occur and the matrix is where the fluid is held. Mitochondria are a part of eukaryotic cells. The, However, despite this vast range in size, shape, and function, all these little factories have the same basic machinery. There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do..
What are the Structure and function of mitochondria?. The transverse tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum systems. Adapted, by permission, from G.R. Hunter and R.T. Harris, 2008, Structure and function of the muscular, To explain the function of spores in terms of chemical and heat resistance To describe characteristics of different types of membrane transport To describe the exact cellular location and serological classification as O antigen of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) To explain how the structure of LPS confers antigenic specificity and toxicity To describe the exact cellular location of Lipid A To explain.
The Power and Importance of Mitochondria TrainingPeaks

Cell Structure Worksheet FM Faculty Web Pages. The wall of a microtubule is composed of 13 parallel protofilaments that enclose a central lumen about 150 A 0 wide. Each protofilaments is made up of a row of globular subunits formed mainly of protein tubulin, each contains one alpha-tubulin molecule and one beta-tubulin molecule. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. They are small structures within a cell that are made up of two membranes and a matrix. The membrane is where the chemical reactions occur and the matrix is where the fluid is held. Mitochondria are a part of eukaryotic cells. The.

16/03/2016В В· Mitochondria structure and function-This lecture explains about the structure and function of mitochondria. This lecture will explain the structure and functions of mitochondria. Mitochondrial structure and function are central to cell physiology and are mutually interdependent. Mitochondria represent a primary target of the alcohol-induced tissue injury, particularly in
explain the term karyotype and mention the karyotype analysis and its significance. BIOLOGY MODULE - 1 Cell – Structure and Function Diversity and Evolution of Life 78 Notes 4.1 THE CELL AND CELL THEORY 4.1.1 Landmarks in cell study Soon after Anton van Leewenhock invented the microscope, Robert Hooke in 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be … Mitochondrial structure and function are central to cell physiology and are mutually interdependent. Mitochondria represent a primary target of the alcohol-induced tissue injury, particularly in
vi State one function of each of the following organelles and explain how these functions are related to each other. 1 mark per explanation) Explain how structure is related to function for each of the following organelles: a) mitochondrion (3 marks) b) chloroplast (3 marks) c) rough endoplasmic reticulum (3 marks) State one way in which the following organelles work together: a) lysosomes and To explain the function of spores in terms of chemical and heat resistance To describe characteristics of different types of membrane transport To describe the exact cellular location and serological classification as O antigen of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) To explain how the structure of LPS confers antigenic specificity and toxicity To describe the exact cellular location of Lipid A To explain
explain the term karyotype and mention the karyotype analysis and its significance. BIOLOGY MODULE - 1 Cell – Structure and Function Diversity and Evolution of Life 78 Notes 4.1 THE CELL AND CELL THEORY 4.1.1 Landmarks in cell study Soon after Anton van Leewenhock invented the microscope, Robert Hooke in 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be … Cell Structure Worksheet Objectives: After working through this worksheet, you should: a) Understand the basic structure of a typical eukaryotic cell. b) Know the structure and function of the plasma membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, vesicles, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria and chloroplasts. c) Be able to label a diagram of a typical
16/03/2016В В· Mitochondria structure and function-This lecture explains about the structure and function of mitochondria. This lecture will explain the structure and functions of mitochondria. 19/10/2008В В· Best Answer: The outer membrane covers the organelle and contains it. The inner membrane folds over many times (cristae). That folding increases the surface area inside the organelle. Many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The increased surface area allows the small
19/10/2008 · Best Answer: The outer membrane covers the organelle and contains it. The inner membrane folds over many times (cristae). That folding increases the surface area inside the organelle. Many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The increased surface area allows the small explain the term karyotype and mention the karyotype analysis and its significance. BIOLOGY MODULE - 1 Cell – Structure and Function Diversity and Evolution of Life 78 Notes 4.1 THE CELL AND CELL THEORY 4.1.1 Landmarks in cell study Soon after Anton van Leewenhock invented the microscope, Robert Hooke in 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be …
MITOCHONDRIAL DNA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION mitochondria. ATA codes for methionine in mitochondria but isoleucine in the cytosol. Finally, AGA or AGG in mitochondria code for a stop codon instead of In the same way that the main building controls a gigantic factory, the nucleus is the control center of the cell. This organelle holds the cell's DNA and the directions for …
ATP Synthase is one of the most important enzymes found in the mitochondria of cells. In this lesson, you'll learn about ATP Synthase structure and function. What is the Structure and Function of the Golgi Apparatus Golgi apparatus : Golgi bodies are absent in prokaryotic cells. Golgi complex is found in all eukaryotic cells except RBCs. Historical Account : Camillo Golgi (1898), a zoologist, observed Golgi bodies in the form of a network in nerve cells of barn owl. Ultrastructure : […]
ATP Synthase is one of the most important enzymes found in the mitochondria of cells. In this lesson, you'll learn about ATP Synthase structure and function. Mitochondria is a special cell that in inside another cell. The function of the mitochondria is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
A mitochondrion produces energy for a cell. Mitochondria (the plural of mitochondrion) are small organelles found in most nucleated cells, including those of plants, animals and fungi. 18/12/2018 · DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria
The wall of a microtubule is composed of 13 parallel protofilaments that enclose a central lumen about 150 A 0 wide. Each protofilaments is made up of a row of globular subunits formed mainly of protein tubulin, each contains one alpha-tubulin molecule and one beta-tubulin molecule. Energy-Linked Functions of Mitochondria 1st Edition Papers Presented at the First Colloquium of the Johnson Research Foundation of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, April 13, 1963